|
Foot Infections
Do not wait until is to late! Symptoms
|
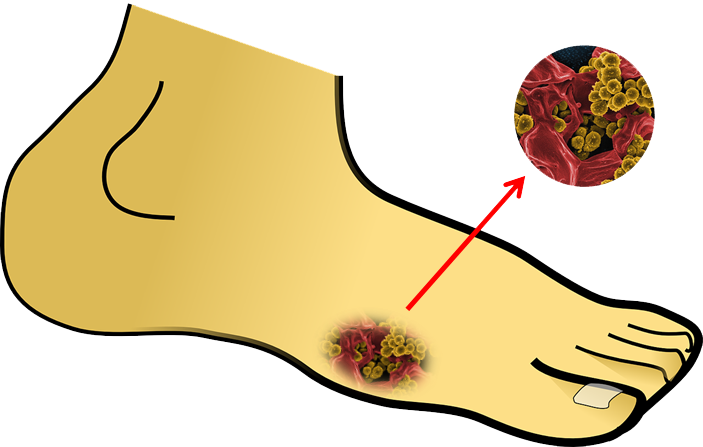
A foot infection can invade part or the entire foot often due to an injury or an open wound. It can be bacterial, fungal, or viral in nature. Check for the telltale symptoms such as pain, inflammation, and pus. The point of this topic is to be sure the public realizes that foot infections require prompt treatment to prevent the infection from spreading and to prevent the infection causing serious or long-term health problems. Your podiatrist should be contacted quickly when you recognize your foot is infected. Causes Foot infections can be caused by virus, bacteria, or fungi. An existing injury or open wound makes the foot vulnerable to different bacteria and viruses that may enter the body through a skin opening. It is very easy for the foot to pick up bacteria and viruses. You should realize that even a little cut can easily get infected. Fungal infections, however, tend to occur differently. Most fungal infections are caused by direct skin contact with contaminated surfaces commonly found in public places and crowded areas. These infections are also contagious and can be easily spread by skin contact. Fungal infections can also easily spread from the foot to another part of the body. Infections of the foot are also identified depending on the specific part of the foot is affected. |
Caution
When left untreated, infection can worsen and may even cause widespread infection in the body. The culprit is bacteria. Bacterial infection can spread very easily, and may begin in the skin and penetrate the deeper layers of soft tissue, bone, and even the blood, causing blood poisoning or septicaemia. | Types The different types of foot infections -- classified as either soft tissue or bone infections -- include:
| Risk Factors There are certain risk factors that may increase a person’s likelihood of getting a foot infection. These include:
|
| Treatment When signs of a foot infection are observed, a person can visit a family doctor or the podiatrist nearest them for the most appropriate treatment. Serious infections require prompt treatment, so it is still best to consult a medical professional. Infections of the foot are initially treated with medications, such as antibiotics, antiviral, and anti-fungal ointments or oral medicines. When caught early, there is a very low risk of serious complications and a high success rate. Most of the time, the treatment period lasts only 7 to 10 days. |




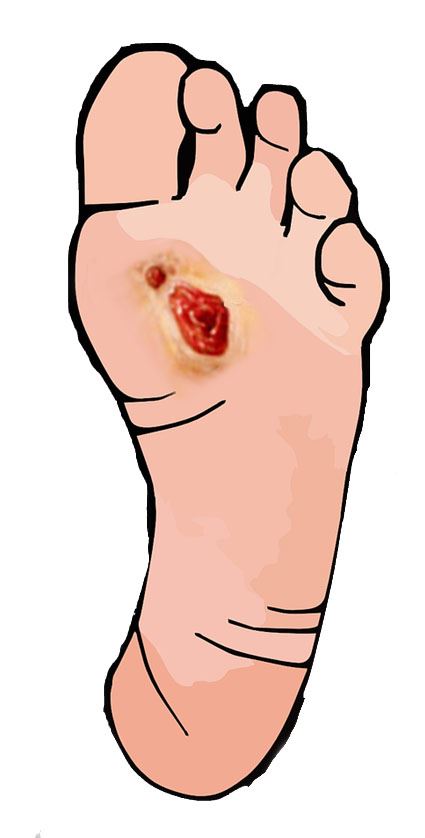 Foot infection can be painful and certainly can be ugly, particularly during the summer when feet are exposed.
Foot infection can be painful and certainly can be ugly, particularly during the summer when feet are exposed.